
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Basic Research
-
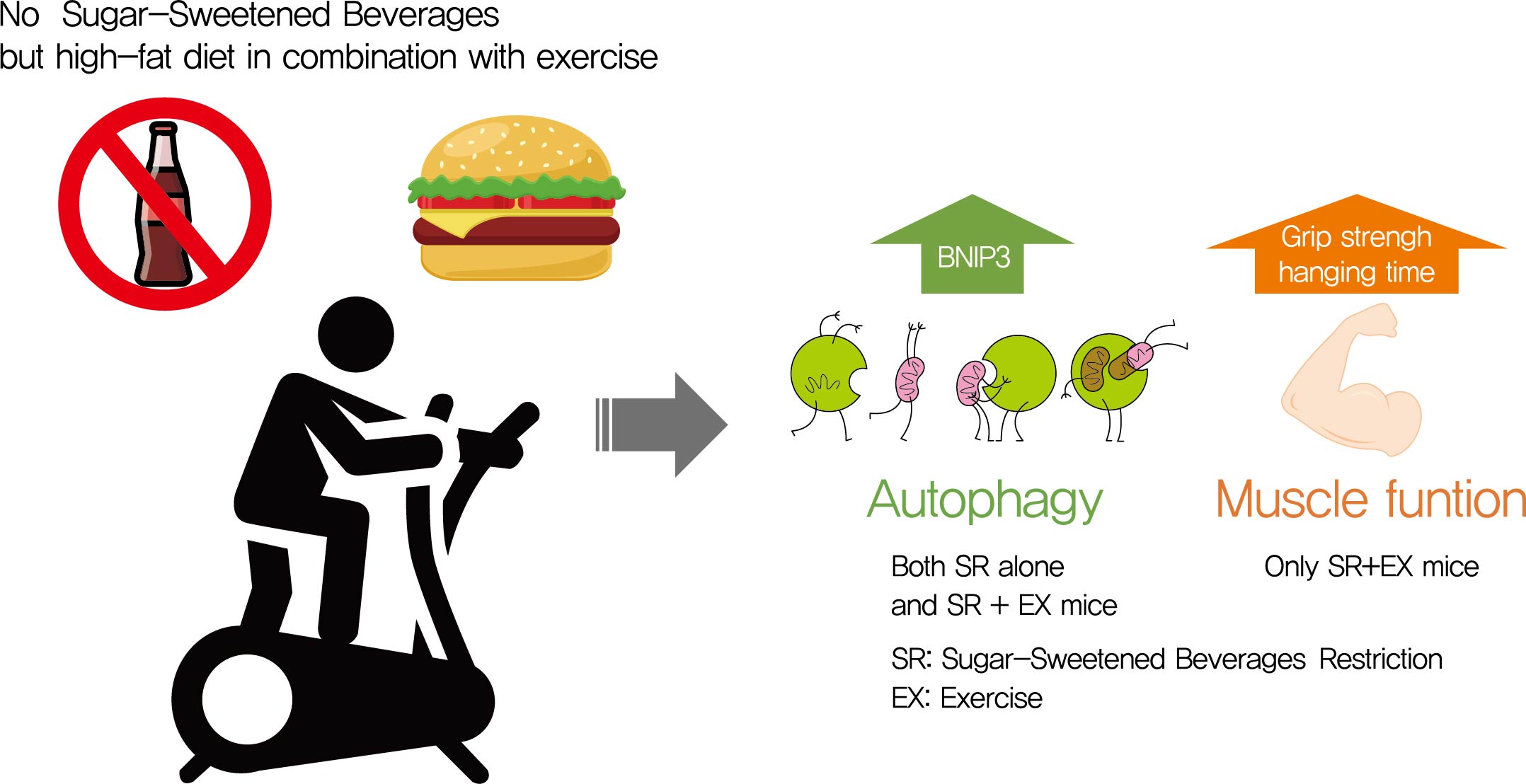
- The Effects of Exercise and Restriction of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages on Muscle Function and Autophagy Regulation in High-Fat High-Sucrose-Fed Obesity Mice
- Didi Zhang, Ji Hyun Lee, Hyung Eun Shin, Seong Eun Kwak, Jun Hyun Bae, Liang Tang, Wook Song
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):773-786. Published online March 25, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0157
- 7,091 View
- 252 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Autophagy maintains muscle mass and healthy skeletal muscles. Several recent studies have associated sugar-sweetened beverage (SSB) consumption with diseases. We investigated whether muscle dysfunction due to obesity could be restored by SSB restriction (SR) alone or in combination with exercise (EX) training.
Methods
Obese mice were subjected to SR combined with treadmill EX. Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test, grip strength test, hanging time test, and body composition analysis were performed. Triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) serum concentrations and TG concentrations in quadriceps muscles were analyzed. Western blot and reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction helped analyze autophagy-related protein and mRNA expression, respectively.
Results
SR alone had no significant effect on fasting blood glucose levels, glucose tolerance, and muscle function. However, it had effect on serum TC, serum TG, and BCL2 interacting protein 3 expression. SR+EX improved glucose tolerance and muscle function and increased serum TC utilization than SR alone. SR+EX reduced P62 levels, increased glucose transporter type 4 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α protein expression, and improved grip strength relative to the high-fat and high-sucrose liquid (HFHS) group, and this was not observed in the HFHS+EX group.
Conclusion
SR induced mitophagy-related protein expression in quadriceps, without affecting muscle function. And, the combination of SR and EX activated mitophagy-related proteins and improved muscle function. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Inter-Organ Miscommunications in T2D Progression
Rajakrishnan Veluthakal, Diana Esparza, Joseph M. Hoolachan, Rekha Balakrishnan, Miwon Ahn, Eunjin Oh, Chathurani S. Jayasena, Debbie C. Thurmond
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(3): 1504. CrossRef - The association between healthy beverage index and sarcopenia in Iranian older adults: a case-control study
Marzieh Mahmoodi, Zainab Shateri, Mehran Nouri, Mohebat Vali, Nasrin Nasimi, Zahra Sohrabi, Mohammad Hossein Dabbaghmanesh, Maede Makhtoomi
BMC Geriatrics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Interplay of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: sarcopenic obesity
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 144: 155577. CrossRef - Association between sugar-sweetened beverage consumption frequency and muscle strength: results from a sample of Chinese adolescents
Yunjie Zhang, Pan Xu, Yongjing Song, Nan Ma, Jinkui Lu
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Muscle strength and prediabetes progression and regression in middle‐aged and older adults: a prospective cohort study
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Yang Yuan, Bo Xie, Zilin Sun, Duolao Wang, Tongzhi Wu
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2022; 13(2): 909. CrossRef - INTENSITY OF FREE RADICAL PROCESSES IN RAT SKELETAL MUSCLES UNDER THE CONDITIONS OF DIFFERENT DIETARY SUPPLY WITH NUTRIENTS
O.M. Voloshchuk, Н.P. Kopylchuk
Fiziolohichnyĭ zhurnal.2022; 68(4): 48. CrossRef
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Inter-Organ Miscommunications in T2D Progression
- Pathophysiology
- The Preventive Effects of 8 Weeks of Resistance Training on Glucose Tolerance and Muscle Fiber Type Composition in Zucker Rats
- Ji-yeon Kim, Mi Jung Choi, Byunghun So, Hee-jae Kim, Je Kyung Seong, Wook Song
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(5):424-433. Published online October 22, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.5.424
- 4,503 View
- 40 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We investigated the therapeutic effects of resistance training on Zucker rats before and after the onset of diabetes to understand the importance of the timing of exercise intervention. We assessed whether 8 weeks of resistance training ameliorated impaired glucose tolerance and altered muscle fiber type composition in Zucker rats.
Methods Five-week-old male Zucker rats were divided into Zucker lean control (ZLC-Con), non-exercised Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF-Con), and exercised Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF-Ex) groups. The ZDF-Ex rats climbed a ladder three times a week for 8 weeks. Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance tests (IPGTT) were performed on the 1st and 8th weeks of training, and grip strength was measured during the last week. We also measured glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) expression by Western blot and immunofluorescence. Moreover, immunohistochemistry was performed to assess muscle fiber type composition.
Results Fasting glucose levels and area under the curve responses to IPGTTs gradually increased as diabetes progressed in the ZDF-Con rats but decreased in the ZDF-Ex rats. Grip strength decreased in the ZDF-Con rats. However, resistance training did not improve grip strength in the ZDF-Ex rats. GLUT4 expression in the ZLC-Con and the ZDF-Con rats did not differ, but it increased in the ZDF-Ex rats. The proportions of myosin heavy chain I and II were lower and higher, respectively, in the ZDF-Con rats compared to the ZLC-Con rats. Muscle fiber type composition did not change in the ZDF-Ex rats.
Conclusion Our results suggest that regular resistance training initiated at the onset of diabetes can improve glucose tolerance and GLUT4 expression without changing muscle morphology in Zucker rats.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Aerobic and resistance exercises affect the BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway, and hippocampal neuron density of high-fat diet-induced obese elderly rats.
Keshvari Maryam, Heidarianpour Ali
Physiology & Behavior.2023; 264: 114140. CrossRef - Nutritive/non-nutritive sweeteners and high fat diet contribute to dysregulation of sweet taste receptors and metabolic derangements in oral, intestinal and central nervous tissues
Yiyuan Zhang, Lu Chen, Jiefang Gao, Yahong Cheng, Fei Luo, Xinying Bai, Hong Ding
European Journal of Nutrition.2023; 62(8): 3149. CrossRef - Anti-osteoporosis mechanism of resistance exercise in ovariectomized rats based on transcriptome analysis: a pilot study
Qing Wang, Heng Weng, Yue Xu, Hui Ye, Yongqi Liang, Lulu Wang, Yutong Zhang, Yujie Gao, Jiayi Wang, Yuchen Xu, Zhiling Sun, Guihua Xu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of resistance exercise training followed by de-training on irisin and some metabolic parameters in type 2 diabetic rat model
Hassan Tavassoli, Ali Heidarianpour, Mehdi Hedayati
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2022; 128(1): 240. CrossRef - Effect of a single bout of resistance exercise on zinc-α2-glycoprotein
Michihiro Kon, Yasuhiro Suzuki
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2022; 128(1): 248. CrossRef - Decreased muscle‐derived musclin by chronic resistance exercise is associated with improved insulin resistance in rats with type 2 diabetes
Mio Shimomura, Naoki Horii, Shumpei Fujie, Kenichiro Inoue, Natsuki Hasegawa, Keiko Iemitsu, Masataka Uchida, Motoyuki Iemitsu
Physiological Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations Between Betatrophin with Irisin and Metabolic Factors: Effects of Two Exercise Trainings in Diabetic Rats
Hassan Tavassoli, Ali Heidarianpour
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2021; 362(5): 496. CrossRef - Resistance exercise affects catheter-related thrombosis in rats through miR-92a-3p, oxidative stress and the MAPK/NF-κB pathway
Cui Wen, Yanping Ying, Huihan Zhao, Qingjuan Jiang, Xiao Gan, Yan Wei, Jiani Wei, Xinxin Huang
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The hypoglycemic mechanism of catalpol involves increased AMPK-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis
Deng-qiu Xu, Chun-jie Li, Zhen-zhou Jiang, Lu Wang, Hong-fei Huang, Zhi-jian Li, Li-xin Sun, Si-si Fan, Lu-yong Zhang, Tao Wang
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2020; 41(6): 791. CrossRef - Long‐term insulin treatment leads to a change in myosin heavy chain fiber distribution in OLETF rat skeletal muscle
Oak‐Kee Hong, Yoon‐Hee Choi, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon, Hee‐Kyoung Jeong, Jang‐Won Son, Seong‐Su Lee, Sung‐Rae Kim, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Soon Jib Yoo
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2019; 120(2): 2404. CrossRef - Mitochondrial dysfunction and inhibition of myoblast differentiation in mice with high‐fat‐diet‐induced pre‐diabetes
Dengqiu Xu, Zhenzhou Jiang, Zeren Sun, Lu Wang, Guolin Zhao, Hozeifa M. Hassan, Sisi Fan, Wang Zhou, Shuangshuang Han, Luyong Zhang, Tao Wang
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2019; 234(5): 7510. CrossRef - Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Glucose Transport and Glucose Metabolism by Exercise Training
Parker L. Evans, Shawna L. McMillin, Luke A. Weyrauch, Carol A. Witczak
Nutrients.2019; 11(10): 2432. CrossRef - Relationship Between Grip Strength and Prediabetes in a Large-Scale Adult Population
Shan Hu, Yeqing Gu, Zuolin Lu, Qing Zhang, Li Liu, Ge Meng, Zhanxin Yao, Hongmei Wu, Xue Bao, Vu Thi Quynh Chi, Shunming Zhang, Mingyue Liu, Yanyan Wang, Liu Wang, Lixiao Zheng, Xiaona Wang, Chunling Tian, Jingzhu Fu, Shaomei Sun, Ming Zhou, Qiyu Jia, Kun
American Journal of Preventive Medicine.2019; 56(6): 844. CrossRef - Resistance exercise improves cardiac function and mitochondrial efficiency in diabetic rat hearts
Tae Hee Ko, Jubert C. Marquez, Hyoung Kyu Kim, Seung Hun Jeong, SungRyul Lee, Jae Boum Youm, In Sung Song, Dae Yun Seo, Hye Jin Kim, Du Nam Won, Kyoung Im Cho, Mun Gi Choi, Byoung Doo Rhee, Kyung Soo Ko, Nari Kim, Jong Chul Won, Jin Han
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology.2018; 470(2): 263. CrossRef - Effects of Resistance Exercise Training on Leptin Receptor (Ob-R), GLUT2 mRNA of the Hypothalamus and GLUT4 mRNA Expression of the Skeletal Muscle in OLETF Rats
Eun-Mi Lim, Se-Hwan Park, Jin-Hwan Yoon
Exercise Science.2018; 27(4): 303. CrossRef - Association of sericin and swimming on the phenotype, motor plate, and functionality of the denervated plantar muscle of Wistar rats
André Junior Santana, Jean Carlos Debastiani, Regina Inês Kunz, Pamela Buratti, Rose Meire Costa Brancalhão, Lucinéia de Fátima Chasko Ribeiro, Márcia Miranda Torrejais, Gladson Ricardo Flor Bertolini
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2018; 14(1): 24. CrossRef - Effects of Treadmill Exercise on Muscle Transcription Factors and TGF-β1 Expression in Aged Rats
Yeon-Hee Kim, Jin-Hwan Yoon, You-Mi Kim
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2017; 56(1): 683. CrossRef - GLUT4 Is Not Necessary for Overload-Induced Glucose Uptake or Hypertrophic Growth in Mouse Skeletal Muscle
Shawna L. McMillin, Denise L. Schmidt, Barbara B. Kahn, Carol A. Witczak
Diabetes.2017; 66(6): 1491. CrossRef - Effects of leucine supplementation and resistance training on myopathy of diabetic rats
Carlos Eduardo C. Martins, Vanessa B. de S. Lima, Brad J. Schoenfeld, Julio Tirapegui
Physiological Reports.2017; 5(10): e13273. CrossRef - Autophagy activation, not peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor γ coactivator 1α, may mediate exercise‐induced improvements in glucose handling during diet‐induced obesity
Megan E. Rosa‐Caldwell, Jacob L. Brown, David E. Lee, Thomas A. Blackwell, Kyle W. Turner, Lemuel A. Brown, Richard A. Perry, Wesley S. Haynie, Tyrone A. Washington, Nicholas P. Greene
Experimental Physiology.2017; 102(9): 1194. CrossRef - α-Motoneurons maintain biophysical heterogeneity in obesity and diabetes in Zucker rats
Christopher W. MacDonell, Jeremy W. Chopek, Kalan R. Gardiner, Phillip F. Gardiner
Journal of Neurophysiology.2017; 118(4): 2318. CrossRef - Relationships among muscle fiber type composition, fiber diameter and MRF gene expression in different skeletal muscles of naturally grazing Wuzhumuqin sheep during postnatal development
Qimuge Siqin, Tadayuki Nishiumi, Takahisa Yamada, Shuiqing Wang, Wenjun Liu, Rihan Wu, Gerelt Borjigin
Animal Science Journal.2017; 88(12): 2033. CrossRef - Evaluation of treadmill exercise effect on muscular lipid profiles of diabetic fatty rats by nanoflow liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry
Jong Cheol Lee, Il Yong Kim, Yeri Son, Seul Kee Byeon, Dong Hyun Yoon, Jun Seok Son, Han Sol Song, Wook Song, Je Kyung Seong, Myeong Hee Moon
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased Muscular 5α-Dihydrotestosterone in Response to Resistance Training Relates to Skeletal Muscle Mass and Glucose Metabolism in Type 2 Diabetic Rats
Naoki Horii, Koji Sato, Noboru Mesaki, Motoyuki Iemitsu, Marcia B. Aguila
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(11): e0165689. CrossRef
- Aerobic and resistance exercises affect the BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway, and hippocampal neuron density of high-fat diet-induced obese elderly rats.
- Effect of Treadmill Exercise on Interleukin-15 Expression and Glucose Tolerance in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats
- Hee-Jae Kim, Jae Young Park, Seung Lyul Oh, Yong-An Kim, Byunghun So, Je Kyung Seong, Wook Song
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(5):358-364. Published online October 17, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.5.358
- 4,086 View
- 34 Download
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Interleukin-15 (IL-15), a well-known myokine, is highly expressed in skeletal muscle and is involved in muscle-fat crosstalk. Recently, a role of skeletal muscle-derived IL-15 in the improvement of glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity has been proposed. However, little is known regarding the influence of endurance training on IL-15 expression in type 2 diabetic skeletal muscles. We investigated the effect of endurance exercise training on glucose tolerance and IL-15 expression in skeletal muscles using type 2 diabetic animal models.
Methods Male Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) and ZDF lean control (ZLC) rats were randomly divided into three groups: sedentary ZLC, sedentary ZDF (ZDF-Con), and exercised ZDF (ZDF-Ex). The ZDF-Ex rats were forced to run a motor-driven treadmill for 60 minutes once a day 5 times per week for 12 weeks. Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT) was performed after 12 weeks. Expression of IL-15 was measured using ELISA in extracted soleus (SOL) and gastrocnemius medial muscles.
Results After 12 weeks of treadmill training, reduction of body weight was observed in ZDF-Ex compared to ZDF-Con rats. Glucose tolerance using IPGTT in diabetic rats was significantly improved in ZDF-Ex rats. Furthermore, the expression of IL-15 was significantly increased (
P <0.01) only in the SOL of ZDF-Ex rats compared to ZDF-Con. Additionally, IL-15 expression in SOL muscles was negatively correlated with change of body weight (R =-0.424,P =0.04).Conclusion The present study results suggest that 12 weeks of progressive endurance training significantly improved glucose tolerance with concomitant increase of IL-15 expression in SOL muscles of type 2 diabetic rats.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beyond muscles: Investigating immunoregulatory myokines in acute resistance exercise – A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Miriam Ringleb, Florian Javelle, Simon Haunhorst, Wilhelm Bloch, Lena Fennen, Sabine Baumgart, Sebastian Drube, Philipp A. Reuken, Mathias W. Pletz, Heiko Wagner, Holger H. W. Gabriel, Christian Puta
The FASEB Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise‐regulated white adipocyte differentitation: An insight into its role and mechanism
Linjing Yan, Liang Guo
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2023; 238(8): 1670. CrossRef - Effects of short-term physical training on the interleukin-15 signalling pathway and glucose tolerance in aged rats
Luciele Guerra Minuzzi, Luciana Renata da Conceição, Vitor Rosetto Muñoz, Renan Fudoli Lins Vieira, Rafael Calais Gaspar, Adelino S.R. da Silva, Dennys Esper Cintra, Leandro Pereira de Moura, Eduardo Rochete Ropelle, Ana Maria Teixeira, José Rodrigo Pauli
Cytokine.2021; 137: 155306. CrossRef - Swimming Program on Mildly Diabetic Rats in Pregnancy
Nathália C. D. Macedo, Isabela L. Iessi, Franciane Q. Gallego, Aline O. Netto, Yuri K. Sinzato, Gustavo T. Volpato, Elena Zambrano, Débora C. Damasceno
Reproductive Sciences.2021; 28(8): 2223. CrossRef - Exercise training and de-training effects on serum leptin and TNF-α in high fat induced diabetic rats
Hamideh Dinari Ghozhdi, Ali Heidarianpour, Maryam Keshvari, Hassan Tavassoli
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise-Induced Myokines can Explain the Importance of Physical Activity in the Elderly: An Overview
Jenny Hyosun Kwon, Kyoung Min Moon, Kyueng-Whan Min
Healthcare.2020; 8(4): 378. CrossRef - Myokine/Adipokine Response to “Aerobic” Exercise: Is It Just a Matter of Exercise Load?
Zihong He, Ye Tian, Pedro L. Valenzuela, Chuanye Huang, Jiexiu Zhao, Ping Hong, Zilin He, Shuhui Yin, Alejandro Lucia
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Overexpression of Interleukin-15 exhibits improved glucose tolerance and promotes GLUT4 translocation via AMP-Activated protein kinase pathway in skeletal muscle
Taku Fujimoto, Ken Sugimoto, Toshimasa Takahashi, Yukiko Yasunobe, Keyu Xie, Minoru Tanaka, Yuri Ohnishi, Shino Yoshida, Hitomi Kurinami, Hiroshi Akasaka, Yoichi Takami, Yasushi Takeya, Koichi Yamamoto, Hiromi Rakugi
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2019; 509(4): 994. CrossRef - Insights from Exercise-induced Cardioprotection-from Clinical Application to Basic Research
Hao Jiang, Beijian Zhang, Daile Jia, Wenlong Yang, Aijun Sun, Junbo Ge
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2019; 25(35): 3751. CrossRef - Myokine Response to High-Intensity Interval vs. Resistance Exercise: An Individual Approach
Zihong He, Ye Tian, Pedro L. Valenzuela, Chuanye Huang, Jiexiu Zhao, Ping Hong, Zilin He, Shuhui Yin, Alejandro Lucia
Frontiers in Physiology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - A systematic review of “myokines and metabolic regulation”
Henry H. León-Ariza, María P. Mendoza-Navarrete, María I. Maldonado-Arango, Daniel A. Botero-Rosas
Apunts. Medicina de l'Esport.2018; 53(200): 155. CrossRef - Exercise benefits in cardiovascular disease: beyond attenuation of traditional risk factors
Carmen Fiuza-Luces, Alejandro Santos-Lozano, Michael Joyner, Pedro Carrera-Bastos, Oscar Picazo, José L. Zugaza, Mikel Izquierdo, Luis M. Ruilope, Alejandro Lucia
Nature Reviews Cardiology.2018; 15(12): 731. CrossRef - Effects of 8 Weeks Resistance Exercise on GSH, SOD, TBARS Activities and GLUT2 mRNA Expression of Pancreas in OLETF Rats
Min-Ki Lee, Jin-Hwan Yoon
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2017; 56(3): 551. CrossRef - Exercise effects on perivascular adipose tissue: endocrine and paracrine determinants of vascular function
B C S Boa, J S Yudkin, V W M van Hinsbergh, E Bouskela, E C Eringa
British Journal of Pharmacology.2017; 174(20): 3466. CrossRef - IL15RA is required for osteoblast function and bone mineralization
Emanuele Loro, Girish Ramaswamy, Abhishek Chandra, Wei-Ju Tseng, Manoj K. Mishra, Eileen M. Shore, Tejvir S. Khurana
Bone.2017; 103: 20. CrossRef - Interleukin‐15 in obesity and metabolic dysfunction: current understanding and future perspectives
Y. Duan, F. Li, W. Wang, Q. Guo, C. Wen, Y. Li, Y. Yin
Obesity Reviews.2017; 18(10): 1147. CrossRef - Effects of interval aerobic training combined with strength exercise on body composition, glycaemic and lipid profile and aerobic capacity of obese rats
Irene Coll-Risco, Virginia A. Aparicio, Elena Nebot, Daniel Camiletti-Moirón, Rosario Martínez, Garyfallia Kapravelou, María López-Jurado, Jesús M. Porres, Pilar Aranda
Journal of Sports Sciences.2016; 34(15): 1452. CrossRef - Exercise-induced alterations in pancreatic oxidative stress and mitochondrial function in type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats
Haider Raza, Annie John, Jasmin Shafarin, Frank C. Howarth
Physiological Reports.2016; 4(8): e12751. CrossRef - Interval aerobic training combined with strength-endurance exercise improves metabolic markers beyond caloric restriction in Zucker rats
V.A. Aparicio, I. Coll-Risco, D. Camiletti-Moirón, E. Nebot, R. Martínez, M. López-Jurado, P. Aranda
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2016; 26(8): 713. CrossRef - IL-15 expression increased in response to treadmill running and inhibited endoplasmic reticulum stress in skeletal muscle in rats
Hong-Tao Yang, Li-Jie Luo, Wen-Jia Chen, Lei Zhao, Chao-Shu Tang, Yong-Fen Qi, Jing Zhang
Endocrine.2015; 48(1): 152. CrossRef - Time course of IL-15 expression after acute resistance exercise in trained rats: effect of diabetes and skeletal muscle phenotype
Mahdieh Molanouri Shamsi, Zuhair Mohammad Hassan, LeBris S. Quinn, Reza Gharakhanlou, Leila Baghersad, Mehdi Mahdavi
Endocrine.2015; 49(2): 396. CrossRef - The search for exercise factors in humans
Milène Catoire, Sander Kersten
The FASEB Journal.2015; 29(5): 1615. CrossRef - Muscle-specific deletion of exons 2 and 3 of theIL15RAgene in mice: effects on contractile properties of fast and slow muscles
Grant O'Connell, Ge Guo, Janelle Stricker, LeBris S. Quinn, Averil Ma, Emidio E. Pistilli
Journal of Applied Physiology.2015; 118(4): 437. CrossRef - Exercise-induced myokines in health and metabolic diseases
Byunghun So, Hee-Jae Kim, Jinsoo Kim, Wook Song
Integrative Medicine Research.2014; 3(4): 172. CrossRef
- Beyond muscles: Investigating immunoregulatory myokines in acute resistance exercise – A systematic review and meta‐analysis

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





